Die casting is one sort of metal casting process through which molten metal is forced to flow into the mold cavity by applying a significant amount of pressure. High accuracy and repeatability can be attained on the final casting part due to the high force applied to the molten metal. The steel molds, also known as dies, are fabricated to produce geometrically complex metal casting components. Although the die casting process consists of many steps, it can be broken down into 7 critical steps. Detailed Step by step process of die casting is discussed below.
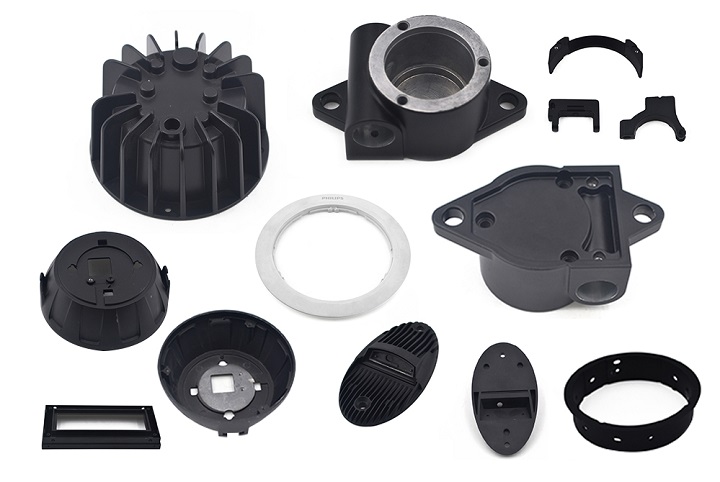

- Step 1: Machine Set-up
The first step in starting the die casting process is to prepare the machine set-up. Basically, this requires the two die halves are closed and clamped together inside the right size of die casting machine, which can generate sufficient force applied to the mold to keep it securely closed while the metal is injected. Also, the die cavity has been heating to an appropriate temperature before applying a refractory coating or lubricant. This lubrication not only keeps the die cool during the production process, but it also inhibits premature solidification and makes it easier to remove the casting part once it’s hardened. Each die half is first cleaned from the previous injection and then lubricated to facilitate the ejection of the next part.
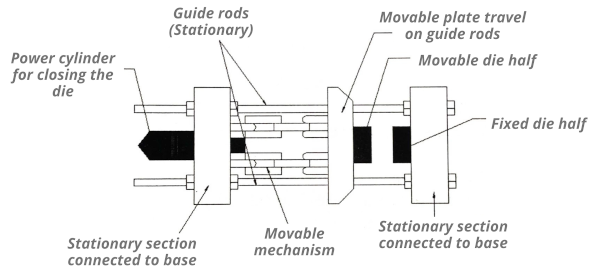
- Step 2: Metal Injection
Upon machine set up ready, the molten metal, which is kept at a certain temperature in the furnace, is transferred and poured to a chamber where it can be injected into the die. The way of transporting molten metal is determined by the type of die casting machine either a hot chamber or cold chamber die casting machine being used. However, they have one thing in common that they both employ a piston or plunger to drive molten metal into the mold cavity via a downward sprue under intense pressure, and such shot metal is held in the die by the holding pressure until it has a chance to solidify.

- Step 3: Shape Solidification
When the molten metal is poured into a die, it starts to cool and solidify soon upon entering the die cavity. The final shape of the casting is formed when the entire cavity is filled and the liquid metal hardens. Need to highlight that sufficient cooling time should be given to assure the casting has solidified before unclamping the die, otherwise, irreversible defects on parts will happen. The proper cooling time can be predicted by several critical factors, including but not limit to the thermodynamic properties of the metal, the maximum wall thickness of the casting, and the complexity of the die.
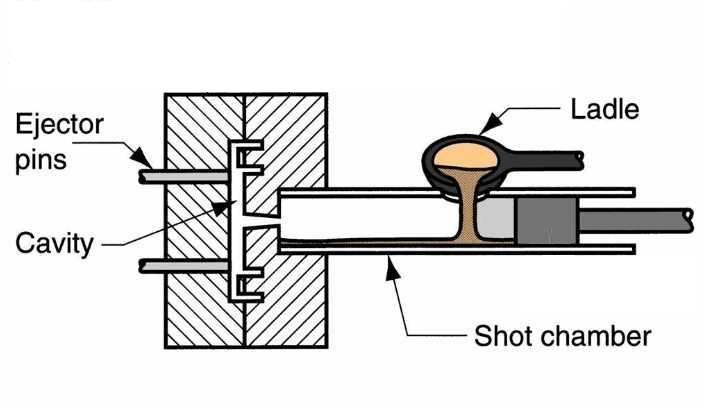
- Step 4: Part Ejection
Once the sufficient cooling time has finished, the die halves can be unclamped and opened, and then the ejection mechanism will push the solidified casting out of the die. The part taking-out can be assisted by manual or a robot hand, and in some situations ejector pins are used to directly push the casting safely out of the gravity die casting machine. Once the part ejection is completed, the operator will continue to clean and lubricate the die cavity surface, so as to facilitate the next casting component.
- Step 5: Part Trimming
The final step of die casting process is trimming. After the metal cools, any excess metal in the sprue and runner, as well as flash, must be manually removed from the final casting, thus creating the desired component net shape. Typically this extra material is trimmed away by cutting or sawing, and sometime by utilizing a trimming press. The trimmed materials can then be discarded or reused in the die casting process, which is determined by the performance requirements of finished casting part.
- Step 6: CNC Machining
It’s worth noting that die casting and CNC machining can frequently collaborate to improve the efficiency of your product line, particularly when the function of a part requires a specific size, shape or geometry, which will dominate the manufacturing process. According to our manufacturing experience, certain features are more difficult to produce with casting. For example, undercuts or interior features will be more challenging to achieve and need complex molds with cores and inserts, and all features on cast parts must have a draft angle, though in some cases it must be straight or perpendicular for good fitting purpose. That’s to say, you can use CNC machining on a die casting component to create tighter tolerances or geometries that can’t be die casted in a direct way.
- Step 7: Surface Coating
Now that you have finished the machining of the casting part, you’re starting to think about surface finish options to meet any function, protection and visual branding needs. It is not always necessary, but most castings do require a surface finish of aesthetic, functional, or protective coating. While there are various surface finishes available and more that are invented daily, we offer our metal casting services with the most popular surface finishes, such as Anodizing, Spraying, Black Oxidizing, Powder Coating and Chrome Plating.

Conclusion
Die casting, as outlined above, is a relatively basic process that may be utilized to produce many complicated metal casting components for a variety of industrial applications. It’s helpful to view of it as a process of conversion or a manner of changing something from one state to another, so it goes like converting molten liquid metals of aluminum or zinc into metal cast parts or components. However, it may appear to be a highly sophisticated and complex procedure to those unfamiliar with the die casting industry, as the operation actually requires solid manufacturing experience and expertise.
To sum up, partnering with a trustworthy die casting partner includes more than just the production of components. At GEMS Manufacturing, we am very specialized in the critical 7 steps to produce finished die casting parts: Machine Set-up -> Metal Injection -> Shape Solidification -> Part Ejection -> Part Trimming -> CNC Machining -> Surface Coating, which provides the possibility to simplify your supply chain and facilitate the efficiency of finished assembly.
ONE-STOP Contract Manufacturing Solutions @GEMS-MFG.
By simplifying the supply chain and maximizing the productivity are key ways to fight global supply chain issues caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, weather disasters, and other unpredictable events. When focusing supply by minimum reliable product provider like GEMS Manufacturing, customers can dramatically simplify the vendor management and speed up product development process, as well as boost quality assurance.
GEMS Manufacturing Ltd, based in Shenzhen China, have been providing Custom Metal, Plastic, Rubber & Electronic Part and Electro-mechanical Assembly Integration Services, which allows our customers to find all their manufacturing needs in one place. At GEMS we understand the importance of cost down manufacturing with flexible solutions, joining us with the industry’s best network of manufacturing talents, tools and facilities. Up-to-date we have shipped hundreds of containers to USA, UK, EURO and other oversea markets.
To learn more about how GEMS Manufacturing can help improve your manufacturing timelines for Integrated Product Development (IPD) and resolve your supply chain challenges, contact us or request a quote when needed.