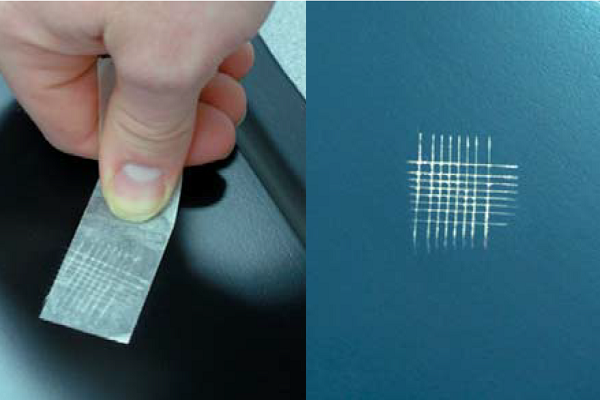
Introduction
Coatings play a pivotal role in protecting surfaces, enhancing aesthetics, and ensuring longevity across various industries. However, the efficacy of a coating is only as good as its quality. To guarantee optimal performance, rigorous testing methods are employed to scrutinize every aspect of a coated surface. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the step-by-step procedures of essential coating surface quality tests. Whether you’re a coating professional, a manufacturer, or simply intrigued by the science behind protective layers, this article will unveil the intricacies of ensuring excellence in coating surface quality.