V. What Information Can One Gain from a DFM Report When Making a New Mold?
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) plays a crucial role in the successful production of molds for various manufacturing processes, including injection molding, die casting, and thermoforming. A comprehensive DFM report provides valuable insights and recommendations that help optimize the mold design for efficient and cost-effective production. Let’s delve into the key information that one can gain from a DFM report when making a new mold:
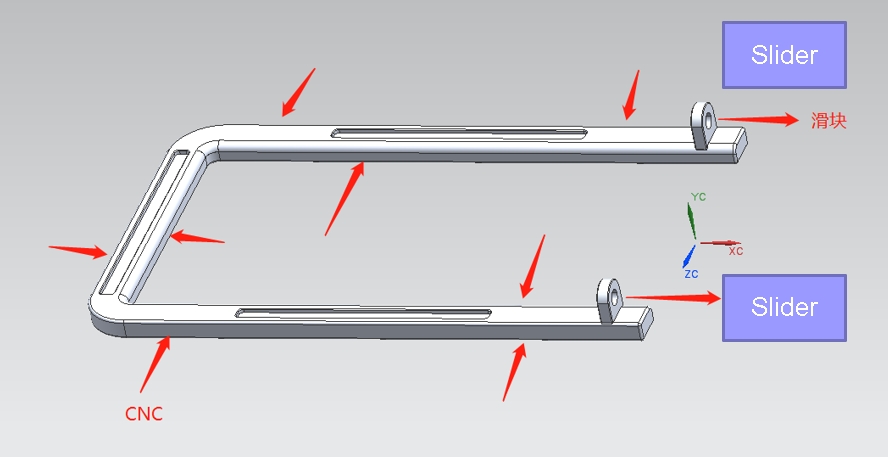
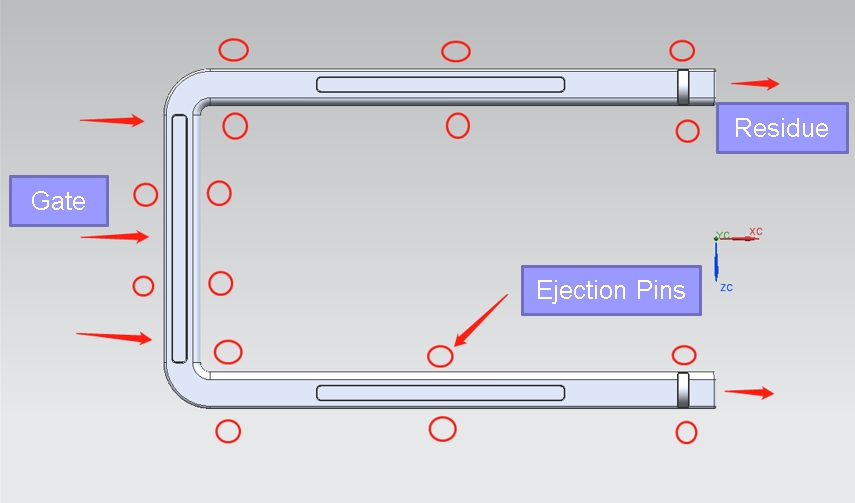
5.1. Gate Position Optimization:
The DFM report evaluates the optimal gate position(s) for the mold, considering factors such as part geometry, material flow requirements, and injection molding parameters.
Recommendations are provided to ensure proper gate location(s) that facilitate efficient material flow, minimize flow length, and prevent part defects.
5.2. Wall Thickness Analysis:
Wall thickness uniformity is critical for moldability and part quality. The DFM report assesses the consistency of wall thickness throughout the part design.
Areas with excessively thick or thin walls are identified, along with recommendations to achieve more uniform thickness distribution and mitigate molding defects.
5.3. Draft Angle Assessment:
Draft angles are essential for facilitating mold release during part ejection. The DFM report evaluates the draft angles incorporated into the part design.
Recommendations are provided to ensure adequate draft angles, preventing sticking or damage to the mold during ejection and improving overall moldability.
5.4. Ejection Pin Placement and Features:
Proper ejection pin placement and design features are crucial for facilitating part ejection from the mold. The DFM report evaluates the ejection pin layout and features.
Recommendations may include adjusting pin placement, adding features such as lifters or slides, or optimizing ejection mechanisms to ensure reliable part ejection without mold damage.
5.5. Cooling System Optimization:
Effective mold cooling is essential for maintaining part quality and minimizing cycle times. The DFM report evaluates the design of the mold cooling system.
Recommendations are provided to optimize cooling channel layout, diameter, and placement, enhancing temperature control and productivity.
5.6. Runner and Sprue Design Analysis:
The runner and sprue system design directly impacts material flow and waste generation. The DFM report assesses the design of the runner and sprue system.
Recommendations aim to minimize runner length, reduce material waste, and optimize gate size and placement for efficient mold cavity filling.
5.7. Material Selection and Processing Parameters Guidance:
Selecting the right molding materials and processing parameters is crucial for achieving desired part quality and production efficiency. The DFM report provides guidance on material selection and processing parameters.
Recommendations may include adjusting processing parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cycle time to optimize part production.
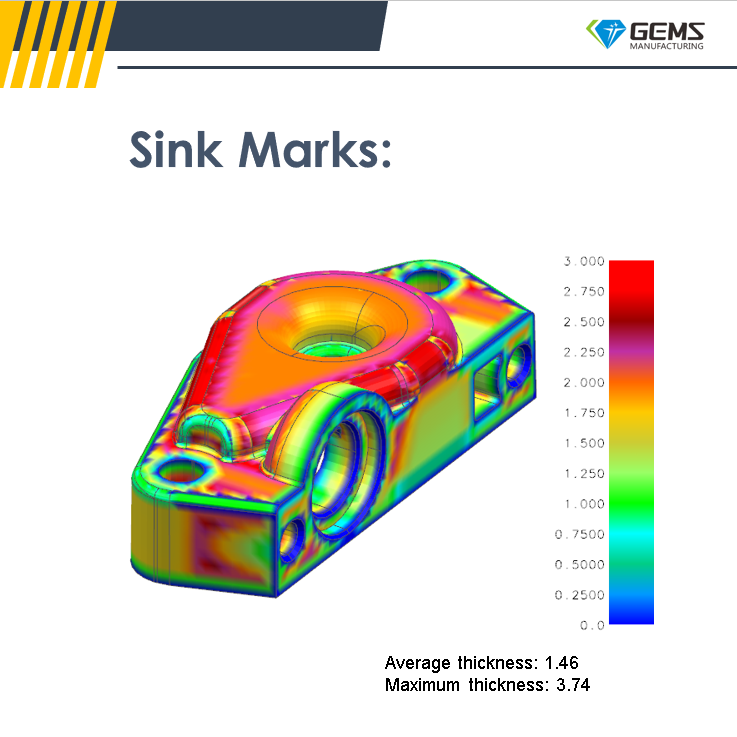
5.8. Material Shrinkage Analysis:
Material shrinkage analysis evaluates how much the material will shrink during the cooling process within the mold. The DFM report includes an assessment of material shrinkage based on the chosen molding material.
Recommendations are provided for adjusting the mold design to compensate for shrinkage, ensuring the final molded parts meet the desired dimensions.
5.9. Tolerance Assessment:
Tolerance assessment determines the allowable deviation from specified dimensions or geometric features on the molded parts. Tight tolerances may be required for critical dimensions.
In the DFM report, tolerance requirements are evaluated based on the functional requirements of the part and manufacturing capabilities. Critical dimensions requiring tight tolerances are identified, with recommendations for achieving them within the mold design.
5.10. Critical Dimensions Evaluation:
Critical dimensions directly impact the part’s functionality or performance and must be carefully evaluated to ensure they can be achieved within the mold-making process.
The DFM report assesses critical dimensions, considering factors such as part geometry, material properties, and manufacturing constraints. Recommendations are provided for adjusting the mold design to achieve critical dimensions.