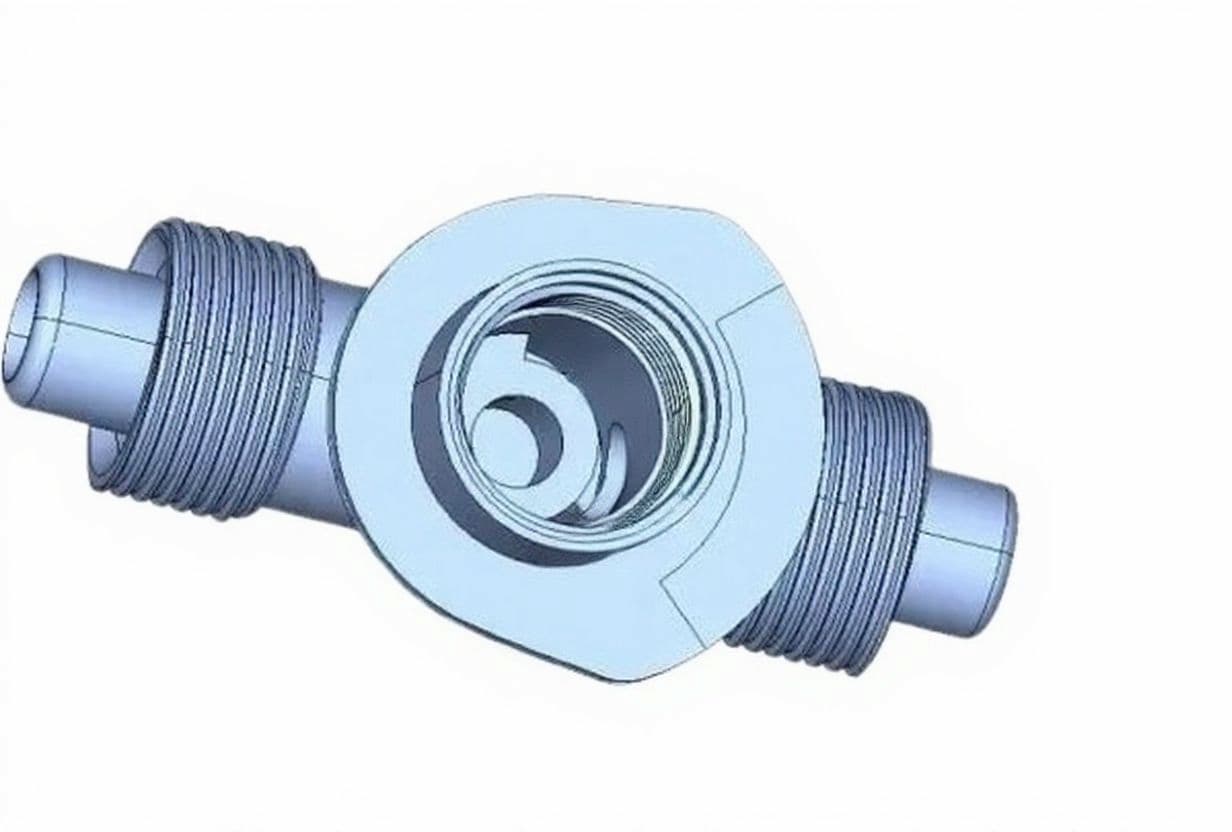
I. Introduction
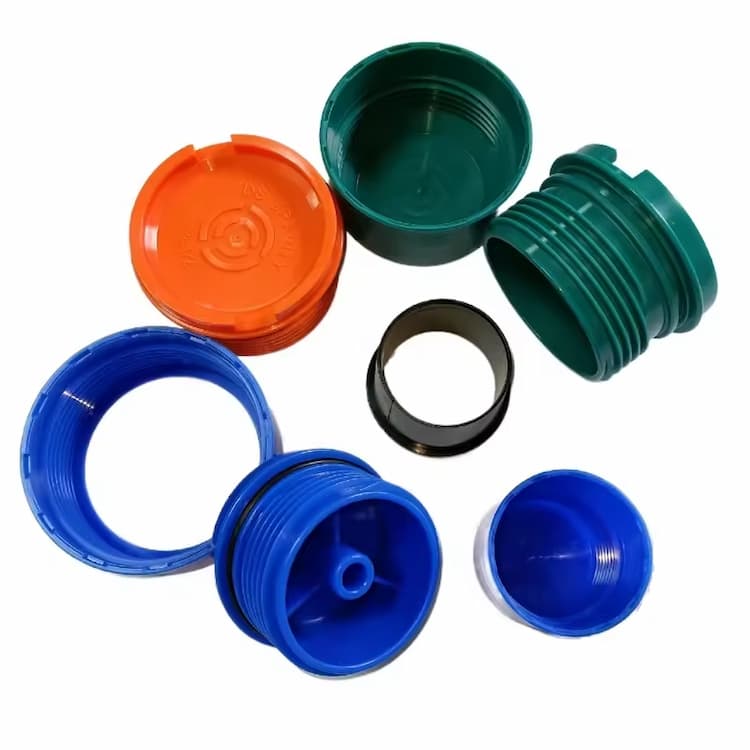
Plastic molded threads are integral features in countless products, providing fastening, sealing, or connection functions without requiring additional machining or assembly steps. By forming threads directly during the injection molding process, manufacturers can achieve significant cost savings, improved dimensional repeatability, and higher production efficiency compared to traditional post-processing techniques such as tapping, thread cutting, or insert installation.
Injection molding of threads is especially beneficial in high-volume industries like packaging, automotive, and consumer goods, where consistent quality and cycle time reduction are critical. With advancements in tooling technology — such as unscrewing cores, collapsible cores, and stripping methods — it is now possible to mold both internal and external threads with high precision, even for complex geometries and miniature designs.
As demand for lightweight, durable, and high-performance plastic components grows, understanding the principles of molded thread design and production has become essential for product designers and mold engineers alike.