I. Introduction to Assemble-to-Order (ATO) Manufacturing
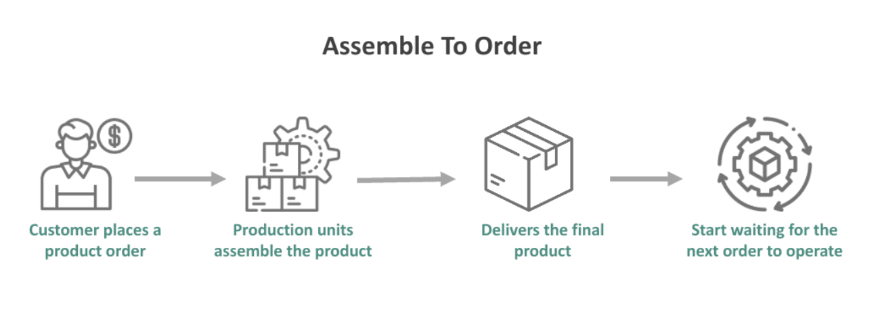
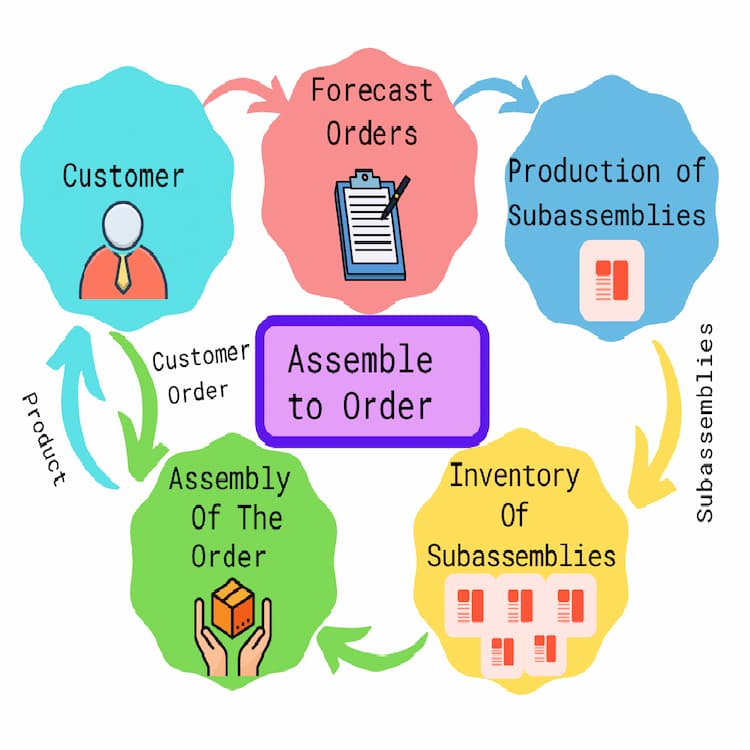
In today’s competitive and fast-paced market environment, businesses are increasingly pressured to deliver customized products quickly and efficiently. Assemble-to-Order (ATO) manufacturing emerges as a strategic solution that bridges the gap between customer personalization and operational efficiency. This approach focuses on assembling finished products only after receiving customer orders, utilizing pre-manufactured and stocked components.
At its core, ATO manufacturing leverages modularity and flexibility. By preparing a comprehensive inventory of pre-assembled components, manufacturers can meet specific customer demands without starting from scratch, significantly reducing lead times. For example, a laptop manufacturer might maintain a stock of standard motherboards, processors, and chassis, combining these modules based on a customer’s configuration request.
Assemble-to-Order is particularly well-suited for industries like consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial equipment, where customization is a competitive differentiator, but production efficiency is critical. By adopting this model, businesses can strike a balance between responsiveness to customer needs and cost-effectiveness, making ATO an essential strategy in modern manufacturing.